Introduction
Loneliness is a growing concern among older adults, affecting their emotional well-being, physical health, and overall quality of life.
While occasional solitude is natural, chronic loneliness can have serious consequences, leading to mental and physical health challenges that diminish independence and happiness.
Why Loneliness is a Growing Concern
Several factors contribute to the increasing prevalence of loneliness in older adults:
- Aging Population: As people live longer, many seniors outlive their spouses, siblings, and close friends, leaving them with fewer social connections.
- Changes in Family Dynamics: Adult children often move away due to career or personal reasons, reducing direct contact with aging parents.
- Retirement and Social Disconnection: Leaving the workforce can lead to a loss of daily social interactions, making it harder to maintain friendships.
- Health and Mobility Challenges: Chronic illnesses, mobility limitations, and cognitive decline can prevent seniors from participating in social activities.
- Increased Use of Technology: While younger generations stay connected online, many older adults struggle to adapt, leading to feelings of exclusion.
The Impact of Loneliness on Mental and Physical Health
Loneliness is more than just an emotional struggle—it has tangible health risks, including:
- Mental Health Decline: Increased risk of depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline, including Alzheimer’s and dementia.
- Weakened Immune System: Chronic loneliness has been linked to higher levels of stress hormones, which can weaken immune function.
- Heart Disease and High Blood Pressure: Social isolation is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and high blood pressure.
- Shortened Life Expectancy: Studies suggest that prolonged loneliness can be as harmful as smoking 15 cigarettes a day.
Understanding Loneliness in Older Adults
Loneliness in older adults is a complex issue influenced by various life changes, health conditions, and social factors. Understanding the root causes and effects of loneliness is essential for developing effective solutions to help seniors stay connected and engaged.
Causes of Loneliness in Older Adults
Several key factors contribute to loneliness in older adults:
- Loss of Spouse, Family, or Friends
- As people age, they often experience the passing of loved ones, leading to a shrinking social circle.
- The absence of lifelong companions can create a deep emotional void and a sense of isolation.
- Physical Limitations and Mobility Issues
- Chronic pain, arthritis, or disabilities can make it difficult for seniors to leave their homes or participate in social activities.
- Reduced physical activity may lead to dependency on caregivers, limiting their ability to interact with others freely.
- Cognitive Decline (Dementia, Alzheimer’s Disease)
- Conditions like dementia can cause seniors to withdraw from conversations and social settings due to memory loss or confusion.
- Loved ones and friends may struggle to communicate with those experiencing cognitive decline, unintentionally increasing their isolation.
- Living Alone or in Care Facilities
- Many seniors live alone, especially after the death of a spouse or family members moving away.
- Even in care facilities, some may feel disconnected due to a lack of personal relationships or insufficient social programs.
- Lack of Social Engagement Opportunities
- Retirement often leads to a loss of structured daily interactions with coworkers and peers.
- Transportation barriers and financial limitations can prevent seniors from attending community events or visiting friends.
- The digital divide makes it difficult for some older adults to use technology to maintain social connections.
B. Effects of Loneliness
Loneliness is not just an emotional burden—it has serious consequences for both mental and physical health:
- Increased Risk of Depression and Anxiety
- Persistent loneliness can lead to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and decreased motivation.
- Anxiety about being alone or feeling like a burden can further isolate seniors.
- Higher Likelihood of Cognitive Decline
- Studies show that social isolation is linked to a higher risk of Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia.
- Regular social interaction helps keep the brain engaged and may slow cognitive deterioration.
- Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases (Heart Disease, High Blood Pressure)
- Loneliness can lead to increased stress, which raises cortisol levels and contributes to high blood pressure.
- Social isolation is associated with an increased risk of stroke, obesity, and weakened immune function.
- Reduced Life Expectancy
- Research suggests that chronic loneliness can be as detrimental to health as smoking or obesity.
- Seniors who lack meaningful social connections may experience a faster decline in overall well-being and lifespan.
Expert-Backed Strategies to Combat Loneliness
Loneliness in older adults is a widespread issue, but it can be alleviated through intentional efforts to foster social connections, encourage engagement, and provide professional support. Below are expert-backed strategies designed to help seniors stay connected and lead fulfilling lives.
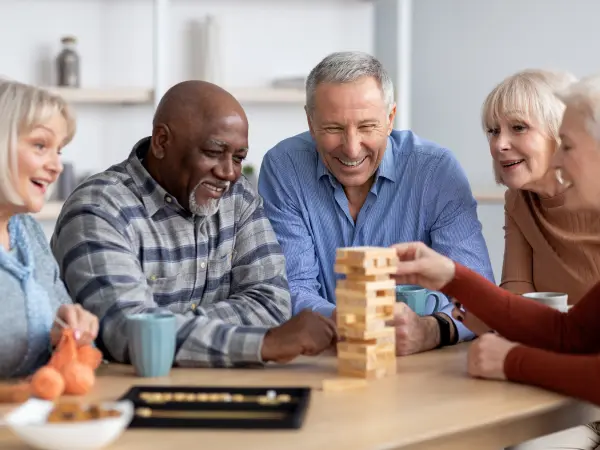
Encouraging Social Interaction
Maintaining relationships and social engagement is crucial for emotional well-being and mental health. Here’s how families, caregivers, and communities can help:
- Importance of Maintaining Relationships
- Strong personal connections can reduce feelings of isolation and improve emotional resilience.
- Encouraging seniors to stay in touch with family, friends, and neighbors helps them feel valued and included.
- Studies show that seniors who maintain social relationships have a 40% lower risk of developing dementia.
- Organizing Regular Family Visits and Calls
- Establishing a routine for phone calls, video chats, and in-person visits can provide consistency and emotional support.
- Family members can set reminders to check in and ensure ongoing communication.
- Community Senior Centers and Social Groups
- Many communities offer senior centers, book clubs, religious gatherings, and hobby-based meetups where older adults can interact and form new friendships.
- Local libraries and recreation centers often host activities like arts and crafts, game nights, and discussion groups.
- Technology-Based Solutions (Video Calls, Social Media)
- Teaching seniors to use video calls (Zoom, FaceTime, WhatsApp) allows them to connect with loved ones from anywhere.
- Encouraging social media use (Facebook, Instagram) can help them stay updated with family events and maintain social ties.
Promoting Purpose and Engagement
Having a sense of purpose can significantly improve seniors’ mental and emotional well-being. Here are some ways to keep them engaged:
- Volunteering Opportunities for Seniors
- Many organizations welcome senior volunteers for roles like mentoring, tutoring, and community service.
- According to a study, seniors who volunteer regularly report higher levels of happiness and lower levels of depression.
- Hobbies and Interest Groups (Gardening, Book Clubs, Music, Art)
- Encouraging seniors to pursue hobbies—such as gardening, painting, knitting, or playing music—can provide social and emotional benefits.
- Joining interest-based groups fosters social connections with like-minded individuals.
- Senior-Friendly Exercise Classes and Wellness Programs
- Group activities like yoga, tai chi, and water aerobics promote physical health while also providing a social outlet.
- Participating in wellness programs helps maintain mobility and boosts overall confidence.
Utilizing Professional Support and Home Care Services
Professional caregivers and support networks can play a crucial role in preventing loneliness by providing companionship and emotional assistance.
- Role of Home Health Aides and Caregivers in Providing Companionship
- Home caregivers offer more than just medical support—they provide companionship, conversation, and daily engagement.
- Studies found that social isolation is a significant risk factor for nursing home placement among older adults, emphasizing the importance of enhancing social contact at home or in community settings to improve health outcomes.
- Support Groups for Grief, Illness, or Aging Concerns
- Support groups allow seniors to share experiences and receive emotional encouragement from others facing similar challenges.
- Many local and online support networks exist for those dealing with grief, chronic illness, or major life transitions.
- Therapy and Counseling Services for Emotional Support
- Mental health professionals can help seniors navigate feelings of loneliness, depression, or anxiety.
- Many therapists now offer virtual counseling, making it more accessible for older adults.
Leveraging Technology for Connection
Technology can be a powerful tool in bridging the gap between seniors and their loved ones while offering opportunities for learning and entertainment.
- How to Introduce Older Adults to Technology (Smartphones, Tablets)
- Providing patient, step-by-step guidance on using devices can make technology more approachable.
- Using large-text interfaces and voice-activated assistants (Alexa, Google Assistant) can enhance accessibility.
- User-Friendly Apps for Seniors (Facebook, Zoom, WhatsApp)
- Facebook helps seniors stay updated on family activities and join interest-based groups.
- Zoom and WhatsApp enable easy video calls with family and friends.
- Online Courses and Virtual Events for Learning and Engagement
- Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Senior Planet offer courses tailored for older adults.
- Virtual religious services, concerts, and discussion forums provide interactive opportunities.
Creating an Age-Friendly Environment
A supportive and accessible environment can encourage socialization and independence while reducing loneliness.
- Designing Accessible Living Spaces That Encourage Mobility
- Ensuring home safety modifications (ramps, handrails, wider doorways) allows seniors to move freely and participate in activities.
- Creating a comfortable, welcoming living space can encourage family visits and social gatherings.
- Intergenerational Programs That Connect Seniors with Younger Generations
- Programs that pair seniors with younger volunteers, students, or mentorship programs foster meaningful relationships.
- Schools, churches, and community centers often facilitate these programs to bridge generational gaps.
- Pet Therapy and Benefits of Companion Animals
- Therapy dogs, cats, and other pets can provide emotional support and companionship.
- Studies show that pet ownership can reduce stress, lower blood pressure, and improve overall mood.
The Role of Family and Caregivers in Combating Loneliness
Recognizing Signs of Loneliness in Older Adults
Identifying loneliness early is crucial for timely intervention. Common indicators include:
- Social Withdrawal: A noticeable decrease in participation in social activities, community events, or family gatherings.
- Changes in Eating Habits: Altered eating patterns, such as skipping meals or lack of appetite, which may signal emotional distress.
- Lack of Interest in Activities: Disinterest in hobbies or activities that were once enjoyable.
- Expressions of Loneliness: Verbal mentions of feeling lonely or lacking companionship.
Taking Proactive Steps to Increase Social Engagement
Enhancing social interactions can significantly reduce feelings of isolation. Strategies include:
- Organizing Regular Activities: Planning family visits, outings, or game nights to foster connection.
- Encouraging Participation in Community Events: Involving older adults in local senior centers, clubs, or religious groups.
- Utilizing Technology: Introducing tools like video calls or social media to maintain connections with distant friends and family.
Encouraging Independence While Providing Support
Balancing assistance with autonomy helps maintain dignity and self-worth.
- Promoting Self-Sufficiency: Encouraging older adults to manage tasks they can handle, fostering a sense of accomplishment.
- Offering Assistance When Needed: Providing help with challenging activities, ensuring it’s supportive rather than overbearing.
- Respecting Personal Choices: Allowing them to make decisions about their daily routines and activities.
Importance of Open Communication and Emotional Support
Building a trusting relationship through open dialogue is essential.
- Active Listening: Paying attention to their concerns and feelings without immediate judgment or solutions.
- Regular Check-Ins: Scheduling consistent times to talk, ensuring they feel valued and heard.
- Encouraging Expression of Emotions: Creating a safe space for them to share their feelings, which can alleviate emotional burdens.
By implementing these strategies, families and caregivers can significantly reduce loneliness in older adults, enhancing their overall quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, addressing loneliness in older adults is essential for promoting their overall health and well-being. Key strategies include:
- Encouraging Social Interaction: Maintaining relationships through regular family visits, participation in community activities, and utilizing technology to stay connected.
- Promoting Purpose and Engagement: Involving seniors in volunteering, hobbies, and exercise programs to foster a sense of purpose.
- Utilizing Professional Support and Home Care Services: Engaging home health aides, support groups, and counseling services to provide companionship and emotional support.
- Leveraging Technology for Connection: Introducing user-friendly devices and apps to facilitate virtual interactions and continuous learning.
- Creating an Age-Friendly Environment: Designing accessible living spaces, promoting intergenerational programs, and considering pet therapy to enhance companionship.
Whether you’re a senior, caregiver, or family member, taking proactive steps to foster social connections can lead to a healthier and more fulfilling aging process. Prioritizing these strategies not only enriches the lives of older adults but also strengthens the fabric of our communities.
At Allgrace Healthcare Solutions, we are dedicated to supporting seniors in building meaningful connections and enhancing their quality of life. Explore our services to discover how we can assist you or your loved ones in combating loneliness and fostering engagement.





0 Comments