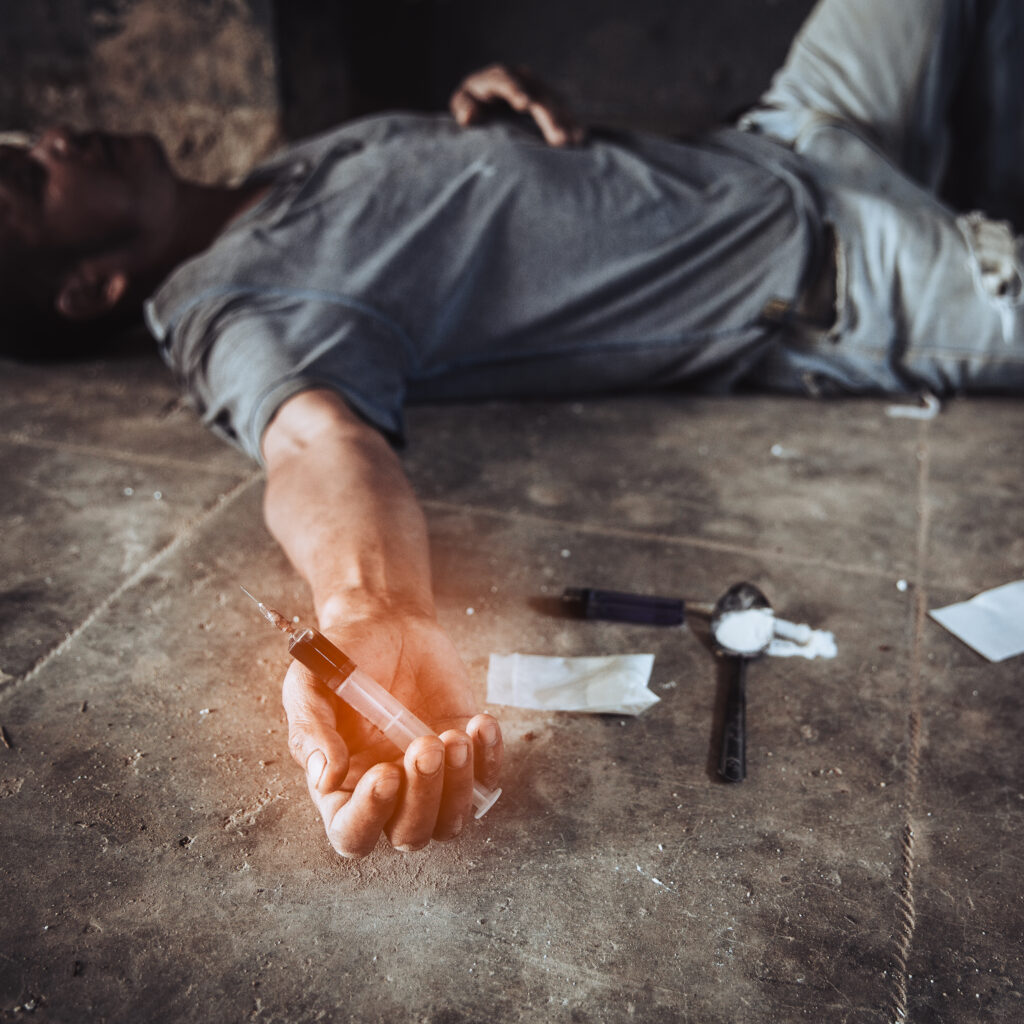

The NSDUH is a survey that’s conducted every year by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). The NSDUH is considered to be the most comprehensive data source on substance abuse in the United States. The NSDUH also collects information on people who are receiving treatment for substance abuse.
The National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) provides statistics on substance abuse in the United States. According to the NSDUH, in 2019, about 20 million people aged 12 or older had a substance use disorder. This represents about 7.4% of the population. Of those with a substance use disorder, 2.5 million had an opioid use disorder, and 1.6 million had a methamphetamine use disorder.
There are many different substances that are commonly abused, but some of the most common ones include alcohol, marijuana, opioids, and stimulants. Alcohol is the most commonly used substance in the United States, and alcohol use disorder is the most common type of substance use disorder. Marijuana is the most commonly used illicit drug in the United States. Opioid use disorder has become an epidemic in the United States, with nearly 2 million people struggling with it. Stimulants like cocaine and methamphetamine are also commonly abused.
There are a variety of factors that can contribute to substance abuse, including genetics, psychological factors, social influences, and environmental factors. Some people are more likely to abuse substances because of their genes, while others may be influenced by their environment or the people they spend time with.
GENETICS
Genetics can play a role in who is more likely to abuse substances. Some people have a genetic predisposition to addiction, which means they may be more likely to develop an addiction if they start using substances. This doesn’t mean that they will definitely develop an addiction, but it does mean that they are at a higher risk.
PSYCHOLOGICAL FACTORS
One of the most important causes of substance abuse is psychological factors. Some people may use substances as a way to cope with stress, anxiety, depression, or other mental health issues. They may feel that using substances helps them to escape from their problems or feel better in the moment. However, substance abuse can actually make these problems worse in the long run.
SOCIAL INFLUENCES
Another major cause of substance abuse is social influences. Peer pressure can play a role in whether or not someone starts using substances. For example, if someone’s friends or family members are using substances, they may feel pressure to do the same. In addition, people may use substances to fit in or feel accepted by a particular group.
ENVIRONMENT
IThe environment can also be a major factor in substance abuse. For example, living in an area with high levels of crime, poverty, or unemployment can increase the risk of substance abuse. Living in a neighborhood with easy access to drugs can also be a risk factor. These environmental factors can make it difficult for people to avoid using substances.
There are a variety of treatment options available for people struggling with substance abuse. The most common type of treatment is called “behavioral therapy.” This type of therapy can help people to identify and change the thoughts and behaviors that lead to substance abuse. Another type of treatment is called “medication-assisted treatment.” This involves using medication to help people stop using substances and manage any withdrawal symptoms they may experience.
BEHAVIOURIAL THERAPY
One type of behavioral therapy is called “cognitive behavioral therapy,” or CBT. This therapy helps people to recognize and change negative or unhelpful thought patterns that lead to substance abuse. Another type of therapy is called “motivational interviewing.” This therapy helps people to identify their reasons for wanting to change and to create a plan for achieving their goals.
CONTIGENCY MANAGMENT
Another type of therapy is called “contingency management.” This therapy uses positive reinforcement, such as rewards, to help people stay on track with their treatment goals. Finally, “family therapy” can be very effective for people with substance abuse issues. This therapy helps families to understand and cope with the effects of substance abuse.
MEDICATION ASSISTANT TREATMENT
There are a few different medications that can be used in medication-assisted treatment. One is called “buprenorphine,” which is a partial opioid agonist. This means that it binds to the same receptors in the brain as opioids, but it produces a weaker effect. This can help people to taper off of opioids without experiencing severe withdrawal symptoms. Another medication is called “methadone,” which is a full opioid agonist. This medication can also help people to taper off of opioids, but it is usually only used in special cases.
One more medication used in medication-assisted treatment is called “naltrexone.” This medication is an opioid antagonist, meaning that it blocks the effects of opioids. This can help to reduce cravings and prevent relapse.
The idea of “recovery” is that substance abuse is a chronic disease, and people can learn to manage it and live fulfilling lives. This means that recovery is not just about abstaining from substances, but also about developing healthy coping skills and building a support network. This approach is often referred to as a “recovery-oriented system of care,” or ROSC.
Instead of seeing it as a moral failing, we can see it as a disease that can be treated and managed. This shift in thinking has led to new programs and policies that support people in their recovery.
Programs that support people in recovery. One type of program is called “harm reduction.” This approach focuses on reducing the negative consequences of substance abuse without necessarily requiring abstinence. Another type of program is called “peer support.” This involves connecting people in recovery with others who have been through similar experiences. Peer support can provide a sense of community and understanding.
Some harm reduction programs provide access to clean needles and other supplies to reduce the risk of blood-borne diseases like HIV and hepatitis. They may also provide education about safer drug use and overdose prevention. Some people believe that harm reduction programs enable drug use, but studies have shown that they actually increase the chances of people seeking treatment.
Another type of program is called “medication-assisted treatment,” or MAT. MAT combines medication with counseling and other types of support to help people overcome addiction. There are several medications that can be used in MAT, including buprenorphine and methadone.
Substance abuse can have a major impact on people’s lives, including their health, their relationships, and their ability to hold a job. Many people who abuse substances also struggle with mental health conditions, such as depression or anxiety. In some cases, substance abuse can lead to homelessness and involvement in the criminal justice system.
There are a number of societal costs associated with substance abuse. One cost is the strain on the healthcare system. People with substance abuse disorders often need more medical care than people who don’t have these disorders. Another cost is lost productivity. Substance abuse can lead to missed work, which means that people are less productive and contribute less to the economy. It can also lead to a higher rate of unemployment.
One cost is the strain on the healthcare system. People with substance abuse disorders often need more medical care than people who don’t have these disorders. Another cost is lost productivity. Substance abuse can lead to missed work, which means that people are less productive and contribute less to the economy. It can also lead to a higher rate of unemployment.
One thing that is often overlooked is the cost of stigma. People with substance abuse disorders may be stigmatized, or viewed negatively, by society. This stigma can make it harder for people to get the help they need. It can also lead to discrimination in areas like housing and employment. Stigma can even lead to a lack of empathy for people with substance abuse disorders.
BOTTOM LINE
According to the NSDUH, in 2019, only about one in five people with a substance use disorder received treatment. This is despite the fact that treatment is effective in helping people recover from substance abuse. One reason for the low rate of treatment may be a lack of access to services. In 2019, only about half of people with a substance use disorder who needed treatment said they thought they could get it if they wanted it.
Substance abuse can have serious consequences for individuals, families, and communities. Some of the negative consequences of substance abuse include financial problems, job loss, homelessness, and family breakdown. Substance abuse can also lead to serious health problems, including addiction, overdose, and death.
Substance abuse is a complex issue with many causes and consequences. There is no single solution to the problem, but treatment can be effective in helping people recover.





0 Comments